VIDEO: Background music starts; shortly after the headline and subhead appear, the glow behind “CD4” animates in.
SUPER: Look CD4WARD: Highlighting the Critical Importance of CD4+ in HIV
VIDEO: CD4+ T-cells visible
VO: CD4 T-cells play an essential role in immune response and control of chronic viral infections.
VIDEO: HIV-1 floats into frame VO: To initiate the viral replication cycle, HIV-1 virions must attach to target CD4 T-cells.
VIDEO: Camera zooms in closer to see gp proteins on HIV-1
VO: This attachment is mediated by viral envelope proteins comprised of gp120 gp41 subunits.
VIDEO: Zoom in on the gp120/gp41 receptors; the receptor transitions between open and closed states
VO: The gp120 gp41 trimer transitions between an open and closed state but CD4 attachment can only occur when the gp120 gp41 trimer is in the open state.
VIDEO: HIV-1 approaches the T-cell membrane; gp120 approaches and binds to the CD4 molecules; gp120 binds to CD4 and HIV starts sinking down and rippling into the T-cell membrane
VO: Binding of the trimer to the CD4 receptor results in a series of conformational changes that enable binding of cell surface co-receptors, CCR5 or CXCR4.
VIDEO: Camera pulls back as we see HIV-1 fusing with the T-cell, sinking down through the membrane, and creating a disruptive aqua-like ripple effect that moves across the surface
VO: Co-receptor binding causes further structural rearrangements that drive fusion of the membrane and allows viral replication to begin.
VIDEO: Close-up of RUKOBIA drug molecule; RUKOBIA drug molecules float toward the CD4+ T-cell with HIV-1 virions circulating
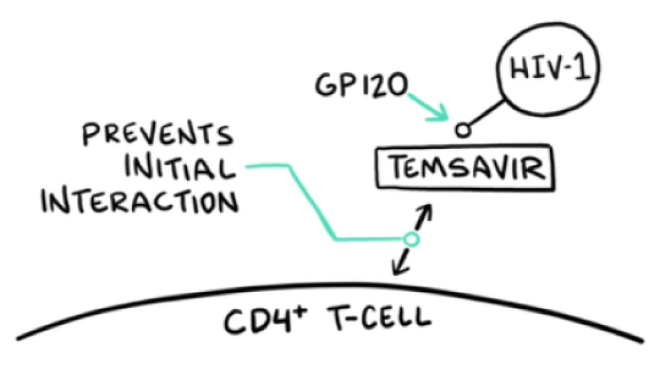
VO: RUKOBIA (fostemsavir) is the first attachment inhibitor with a first-in-class mechanism of action that blocks HIV-1 from interacting with host CD4 cells.
VIDEO: Drug molecule approaches HIV that is heading towards T-cell; drug molecule intercepts HIV by binding to gp120 on the envelope of HIV-1; RUKOBIA binds to gp120, which initiates a “frosted glass” effect that spreads across gp120 and then continues over HIV virion
VO: At a granular level, temsavir, the active moiety of RUKOBIA, binds to the gp120 subunit within the HIV-1 envelope. This locks the gp120 gp41 trimer in the closed state.
VIDEO: “Frosted glass” effect spreads across HIV to represent that it’s suspended in the closed state and cannot bind to CD4; gp120 is unable to bind and HIV floats away
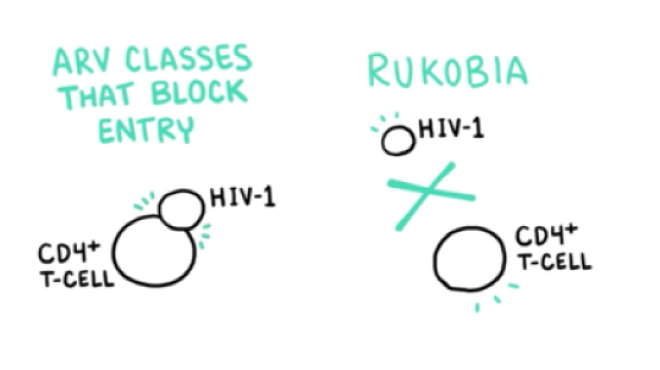
VO: This action selectively inhibits any interaction between the HIV-1 virion and cellular CD4 receptors.
VIDEO: RUKOBIA drug molecules approach HIV, and we see subsequent frosted glass effect spreading over them as result of binding to gp120s; HIV virions with the frosted glass effect
VIDEO: RUKOBIA rotates and sparkles in space
VO: This novel mechanism of action makes RUKOBIA the only ARV to prevent HIV-1 from attaching to CD4 cells.
VIDEO: Camera pulls back through a field of RUKOBIA molecules
VO: There is an unmet need to optimize an effective regimen for heavily treatment-experienced people living with HIV failing their current ARV regimen—whether due to resistance, intolerance, or other safety considerations.
VIDEO: Headline fades into frame with RUKOBIA molecules floating in space; the “CD4” text is animated to glow behind it
SUPER: LOOK CD4WARD
VIDEO: References fade into frame
SUPER: Reference list
VIDEO: RUKOBIA and ViiV logos fade in with trademark line; background music fades out
SUPER: For US Healthcare Professionals only. Trademarks are owned by or licensed to the ViiV Healthcare group of companies. ©2025 ViiV Healthcare or licensor. PMUS-FSTVID250005 May 2025 Produced in USA.